Original source: Shanghai Shutu Blockchain Research Institute
At the Conflux OS operating system conference held on September 21, 2022, Shanghai Shutu Blockchain Research Institute released the Conflux OS operating system for Web3.0. The conference was guided by Shanghai Science and Technology Commission and Shanghai Xuhui District People's Government, hosted by Shanghai Shutu Blockchain Research Institute, and co-organized by Hunan Xiangjiang Shutu Information Technology Innovation Center.
At the press conference, Professor Long Fan, the founder of Conflux Treemap and President of Shanghai Treemap Blockchain Research Institute, introduced the Conflux OS product and product development background; Dr. Yang Guang, Research Director of Shanghai Treemap Blockchain Research Institute, from the technical Angle explains Conflux OS in detail.
Background
In today's world, technological innovation is the primary productive force, and the Internet revolution is our closest and most intuitive experience of this innovative idea. It has been 53 years since the birth of the world Internet, and 28 years of China's full-featured Internet access. In the past 28 years, China's Internet has developed tremendously. It has quickly become the first driving force of productivity, driving the high-quality development of China's economy in an all-round way. The digital economy has become a new engine, new bright spot, and new driving force for China's economic development. By 2021, the scale of my country's digital economy will reach 45.5 trillion yuan, ranking second in the world in total.
The Internet is a major revolution in human communication technology and has had a profound impact on human society. With the current iterative innovation of various information technologies, the Internet is showing a trend of evolution to the next-generation Internet. This evolution may trigger a new round of information revolution, which will further profoundly change people's life, work and all aspects of society. In 1993, on the eve of the advent of Web1.0, the Clinton administration of the United States issued a strategic plan of "National Information Infrastructure" to vigorously build a "highway" in the information age, thereby gaining the global leadership of Web1.0 and Web2.0. After 30 years of development, the Internet is now at an important point in the evolution from Web 2.0 to Web 3.0.
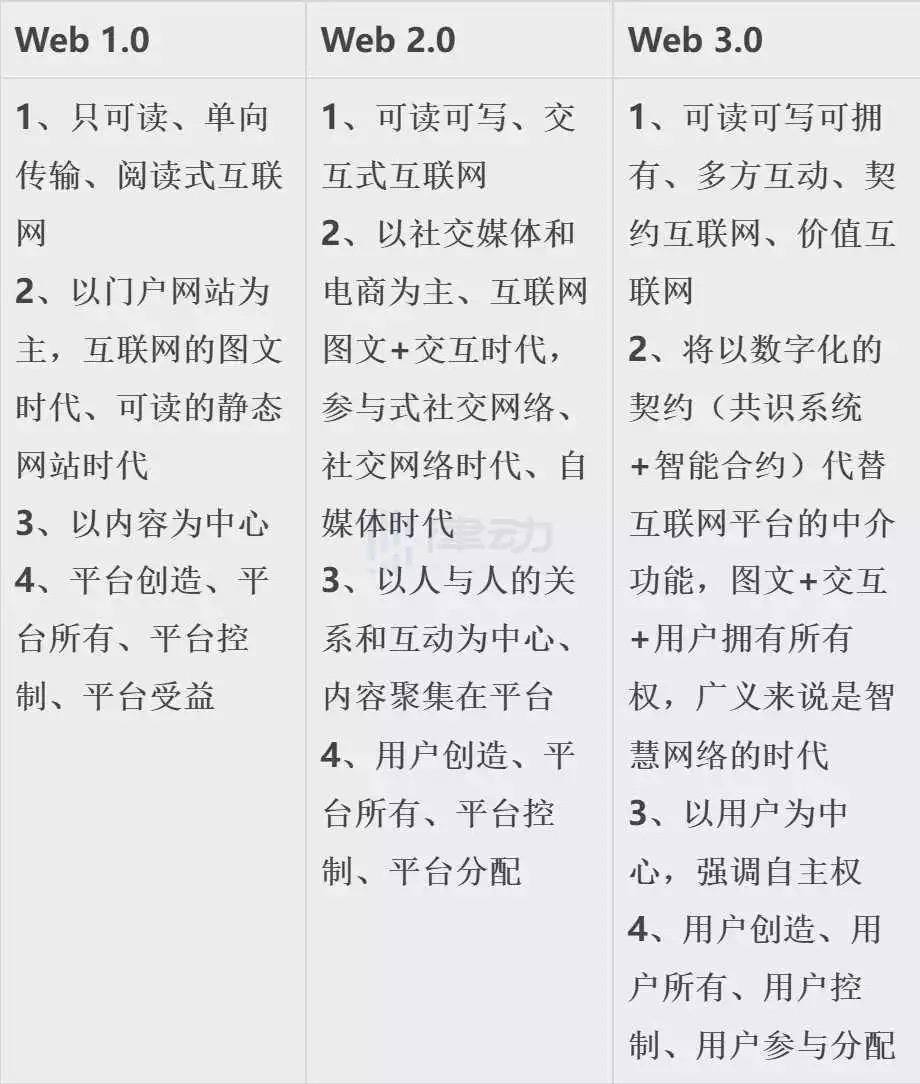
Different from the common way of dividing generations by technical indicators (such as 2G/3G/4G/5G in the field of mobile communication or 28nm/16nm/7nm process in the field of chips, etc.), Web1.0, Web2.0, Web3 The division of .0 is not in technical indicators, but in the form in which the data is generated and processed. If the former is classified as the development stage of productive forces, the latter actually corresponds to different stages of production relations in the digital world.
To put it simply, Web 1.0 is characterized by a reading-based "Internet of Information", professional websites (such as portals) are responsible for producing content, and users are consumers of content; Web 2.0 is characterized by "readable + accessible "Social Network" and "Interactive Internet" in "Writing", emphasizing "interaction, sharing, relationship", with the development of mobile Internet and online platforms such as YouTube, Facebook, Twitter, WeChat, etc., users as the main producers of content spread on the Internet own works (including text, pictures, videos, etc.) and interact with other users. Regardless of Web1.0 or Web2.0, Internet platforms can obtain the right to formulate rules and distribute benefits by virtue of their control over data and algorithms. Users lack autonomy in front of Internet platforms.
Web3.0 is characterized by the "Internet of Value" and "Internet of Contracts" of "readable + writable + possessable", emphasizing user-centered "autonomy", empowering users to manage digital identities, control personal data, and supervise algorithm applications autonomy to reshape the trust and collaboration of Internet participants. Therefore, Web3.0 replaces the "black box" of the Internet platform with rules written in code, which makes the process of information processing fairer and more transparent, and protects the creator's ownership and revenue rights of works through digital contracts, which can realize the ever-changing Digital content productivity is more compatible with digital production relations.
In order to realize the autonomy pursued by Web3.0, it is no longer necessary to rely on the centralized server of the Internet platform to process data information, and a neutral and credible computing platform must be established as the digital infrastructure of Web3.0, which is open, transparent, and reliable. The information method completes the replacement of centralized platforms in all aspects of data collection, circulation, storage, processing, and distribution. The blockchain consensus system is such a computing platform: the blockchain consensus nodes jointly maintain the data recorded in the blockchain ledger, perform calculations according to the smart contract code and reach a consensus on the result, which is actually a virtual computer implemented in the consensus system. , which can provide neutral and trusted data storage and computing services to the outside world. By invoking the blockchain consensus system, Web3.0 applications can ensure the credibility of key data and key computing links from being maliciously controlled and tampered with.
But on the other hand, calling the blockchain consensus system to complete data storage and computing tasks is different from the traditional new computing model based on centralized servers (including distributed systems and cloud computing), and the technical threshold is relatively high, especially when it comes to suitable It will be more complicated when multiple blockchain consensus systems are deployed. It is not a good solution to let application developers directly face the consensus storage and consensus calculation at the bottom of Web3.0, and develop applications for each blockchain system, which will inevitably waste a lot of energy. Therefore, in order to reduce the threshold and cost of application research and development, and let application developers focus more on business logic, it is necessary to technically manage the underlying distributed, multi-source heterogeneous computing resources in a unified manner, and provide application developers with encapsulated interfaces.
Such a system that uniformly manages and schedules underlying computing resources and provides a development and operating environment for upper-layer applications is called an "operating system" in the PC era and the smartphone era. With the evolution of the Web3.0 information processing paradigm, the development of the Web3.0 industry also needs a matching operating system. This is the background behind the development of the Conflux OS operating system.
Conflux OS operating system
Conflux OS is a network operating system that follows the Web3.0 computing paradigm to manage and schedule the underlying computing resources of Web3.0. The carrier of its operation is not a single computer or smartphone, but the entire Web3.0 network. Roughly speaking, the core computing resources of Conflux OS do not come from local hardware such as CPU, memory, hard disk, etc., but the public services existing in the Web3.0 network, including the data storage and computing power provided by the blockchain consensus system, Data storage services provided by IPFS, computing services provided by third-party service providers (based on TEE, MPC, FHE and other trusted computing technologies), etc. Conflux OS guarantees the neutrality and trustworthiness of data storage and computation by managing and scheduling these resources from Web3.0 network public services, thereby helping Web3.0 applications to achieve user autonomy over identity, data and algorithms.
The Conflux OS operating system is divided into four layers:
User client: in the form of a program running locally (mobile phone, PC), it provides users with access to Web3.0 resources and applications, including Web3.0 browsers, application markets, personal accounts and digital identity management and other functions, and provide a graphical interface for running other Web3.0 applications. Currently, Conflux OS mainly provides mobile apps as user clients.
Productivity tools: productivity tools for Web3.0 application operators, including NFT kits, DAO community kits, etc., through a graphical interface to achieve out-of-the-box and code-free development, reducing the technical threshold for producing and using Web3.0 products . The kit also provides an extensible API interface to support lightweight custom development and a variety of product forms. Conflux OS will also launch productivity tools for other application scenarios.
Development environment: For Web3.0 application developers, Conflux OS will provide the front-end component library of UI interaction layer, the development framework for middle and back-end business, middleware in the form of SDK or Web API, as well as test network, Basic services such as sandbox environment. Web3.0 application developers can implement custom business logic within the existing development framework, and complete development tasks quickly and efficiently in the form of low-code development.
The underlying infrastructure: manage and schedule computing resources from the Web3.0 network, including selecting and locating blockchain consensus nodes, reading and writing data based on blockchain systems, and performing computing tasks. Conflux OS will first access the treemap public chain and treemap alliance chain at the bottom layer as the infrastructure for consensus storage and consensus computing for Web3.0 applications, and will also access other Web3.0 resources such as Ethereum and IPFS in the future.
The application layer interface of the Conflux OS operating system will implement the international standard of IEEE P3217 "Blockchain System Application Interface Specification" (the standard is led by the Shanghai Shutu Blockchain Research Institute), which provides the greatest support for other Web3.0 applications. degree of compatibility.
Significance of Conflux OS
Similar to the operating systems of PCs and smartphones, Conflux OS, as a Web3.0 operating system, realizes a reasonable division of labor among system developers, application developers, and operators. It reduces the technical cost of developing and operating Web3.0 applications, allowing developers and operators to focus more on business logic, which is conducive to the vigorous development of the Web3.0 application ecology and even the entire "metaverse" industry.
In response to the current situation of multi-chain coexistence and rapid technological iteration in Web3.0 and Metaverse environment, Conflux OS provides a unified interface to the application layer by encapsulating the underlying heterogeneous blockchain system, which can effectively solve the problem of cross-chain information being difficult to communicate, multiple Chain deployment and adaptation costs are high. By integrating the underlying blockchain system, Conflux OS is expected to bridge the current fragmented ecology of the Web3.0 industry to a certain extent.
Conflux OS also provides users with a one-stop Web3.0 terminal entry, which not only assists users to manage personal digital identities conveniently and quickly, but also provides audited, safe and reliable applications through the Web3.0 application store to avoid users from high-risk applications. , phishing websites, etc. suffer losses.
To sum up, the significance of Conflux OS for Web3.0 and the Metaverse industry is to improve production efficiency and promote the development of application ecology through division of labor and cooperation; the significance to users is to provide a convenient, easy-to-use, and secure terminal entry, as well as rich and diverse Web3.0 application.
Supplementary Information: Treemap Blockchain
The tree graph consensus algorithm is a high-performance consensus sorting algorithm that uses a tree-graph structure (Tree-Graph) to organize blocks. This algorithm can reach a consensus on the sorting of concurrent blocks, so as to not sacrifice openness and security , which breaks through the performance bottleneck of the existing blockchain system in terms of transaction throughput (TPS) and confirmation time (Confirmation Latency). On a blockchain network consisting of tens of thousands of consensus nodes using proof-of-work (PoW), the treemap consensus algorithm achieves a high throughput rate of over 6000 TPS while reducing confirmation time to within 23 seconds. For comparison, Bitcoin and Ethereum have throughput rates of only 7 TPS and 40 TPS, and require confirmation times of up to 1 hour and 10 minutes, respectively. In the field of the underlying technology of the blockchain, the tree graph consensus algorithm has broken the monopoly of Western countries, and its innovation and advancement have won widespread attention from academia and industry, and it has become the Diem (formerly known as Libra) of Facebook. The only Chinese-led blockchain project mentioned in the technical white paper of the alliance chain project.
The treemap public chain (Conflux) is a high-performance public blockchain underlying infrastructure based on the treemap consensus algorithm. The designed throughput rate is 3000 TPS, which is 428 times that of Bitcoin and 75 times that of Ethereum. The main network of the treemap public chain was officially launched on October 29, 2020. At present (as of September 15, 2022), the total number of accounts exceeds 24 million, the total number of transactions processed exceeds 114 million, and the number of online consensus nodes exceeds 5,000 (ranked among the top three in the world), with world-leading performance and safety. With the support of stable cross-chain services and rich developer tools, the treemap public chain has incubated hundreds of ecological projects.
The treemap consortium chain is a high-performance blockchain underlying infrastructure optimized for consortium chain scenarios. Tested by the China Electronics Standardization Institute (CESI Lab), the treemap consortium chain version 1.0 can achieve a throughput rate of more than 20,000 TPS in a network of 100 consensus nodes, reaching the world's leading level in both scale and performance. When the treemap alliance chain achieves the above-mentioned network scale and consensus performance, the hardware configuration of a single consensus node only needs 8-core CPU/16 GB memory/100M network, which is far lower than the hardware requirements of other similar alliance chains in China. "The highest alliance chain.
Supplementary Information: IEEE P3217 Standard
IEEE P3217 "Blockchain System Application Interface Specification" defines and regulates the interface between the blockchain layer and the application layer of the blockchain system, with the purpose of standardizing the interaction mode between the blockchain application and the blockchain consensus system , so that application layer developers can be freed from the details of the underlying consensus system and only need to focus on business logic without having to be familiar with the differences of each blockchain system.
If the blockchain layer and application layer of the blockchain system are analogous to the operating system and application software of a traditional computer, the IEEE P3217 standard acts like IEEE 1003 "Portable Operating System Interface" that defines the interface of the UNIX operating system (Portable Operating System Interface in English, abbreviated as POSIX) standard, also known as ISO/IEC 9945 standard.
POSIX is a general term for a series of API standards defined by IEEE in order to facilitate the development and operation of software on different versions of the UNIX operating system. Software developed in accordance with the POSIX standard can be easily ported to all POSIX-compliant operating systems, which is especially important for open source software that does not depend on a specific operating system, so the standard has been widely recognized by the industry and open source software community. Among the common operating systems, macOS, Solaris, etc. have obtained the official POSIX certification of the IEEE. Although Android, Linux, and Darwin (the core of macOS and iOS) have not been officially certified, they are actually compatible with the POSIX standard. Microsoft's Windows NT is also partially certified. Implements the POSIX standard.